| Category |
Coursework |
Subject |
Management |
| University |
Aston University |
Module Title |
BNM810 Operations Management |
BNM810 Module aim
- Based on the module’s UMD, by completing this coursework, you should be able to:
- Explain the strategic importance of operations management and its theoretical bases in managing organisational resources.
- Explain the key decision-making areas in operations management and apply them to different contexts.
- Evaluate the contribution that operations management makes to procurement, supply chain management and organisational performance, and be able to apply some practical methods, and
- Examine the contribution that operations management makes to performance and organisational improvement.
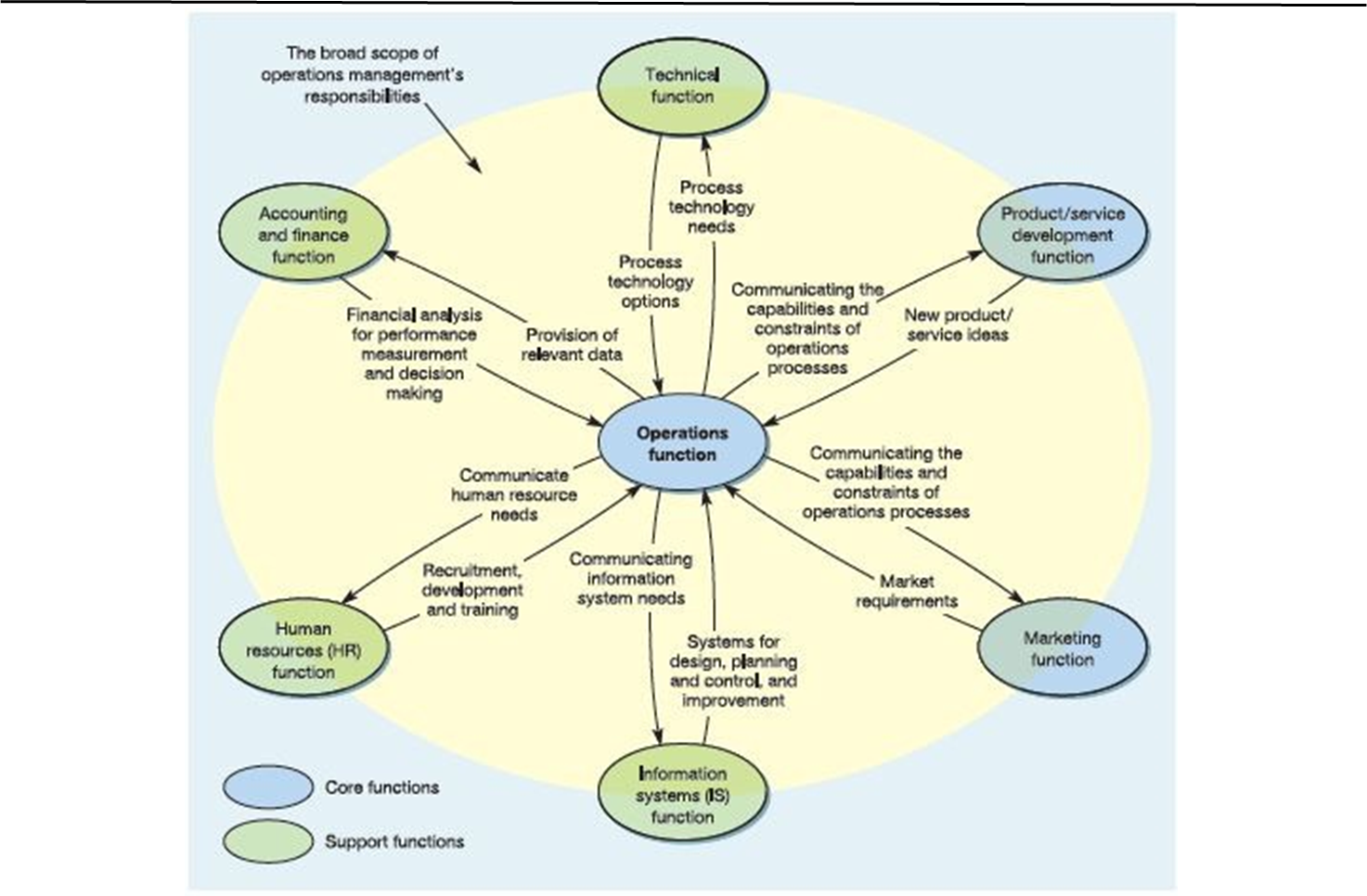
The Operations Function
Operations
- How organisations create and deliver products and services
- Transformation process
- Links with marketing and product development
Operations Management Definition

Operations management is the activity of managing the resources that are devoted to the production and delivery of products and services
Why Study Operations Management?
- OM is one of the three major functions of any organisation. We want to study how people organise themselves for a productive organisation
- We want and need to know how goods and services are produced
- OM is such a costly part of an organisation
A General Model for Operations
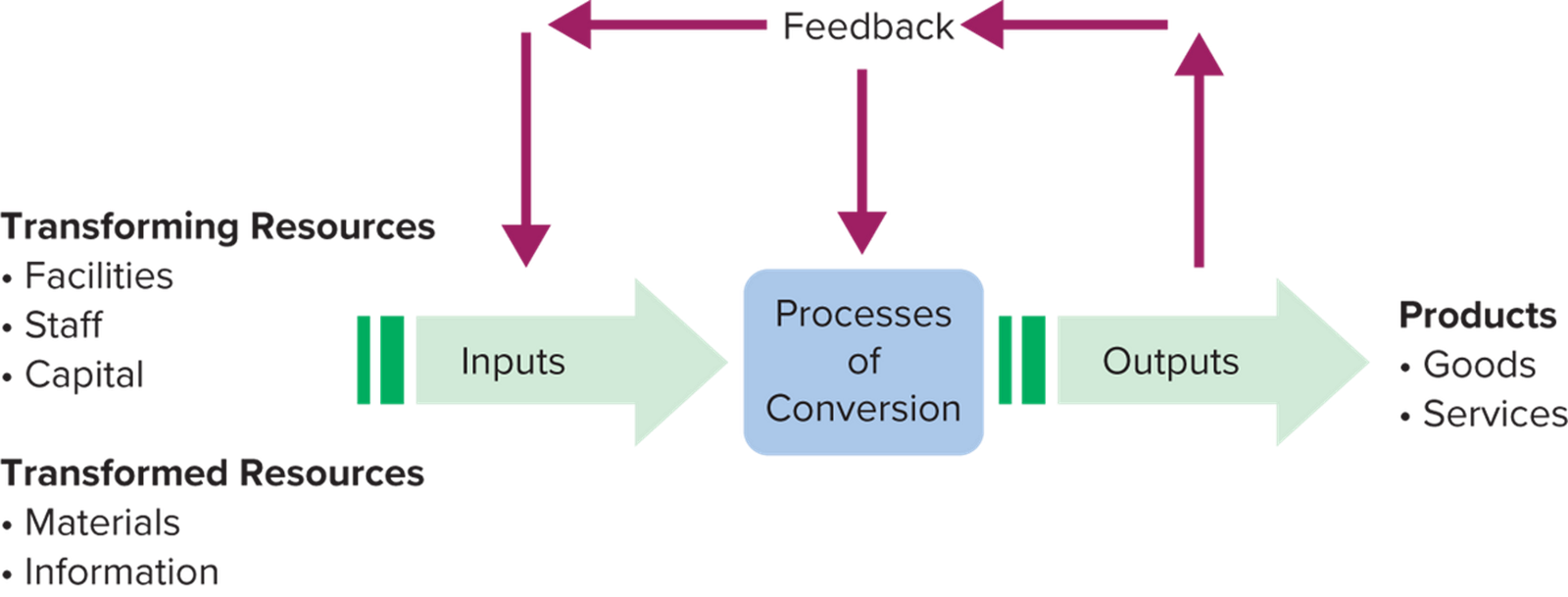
All Operations are Input Transformation, Output Process
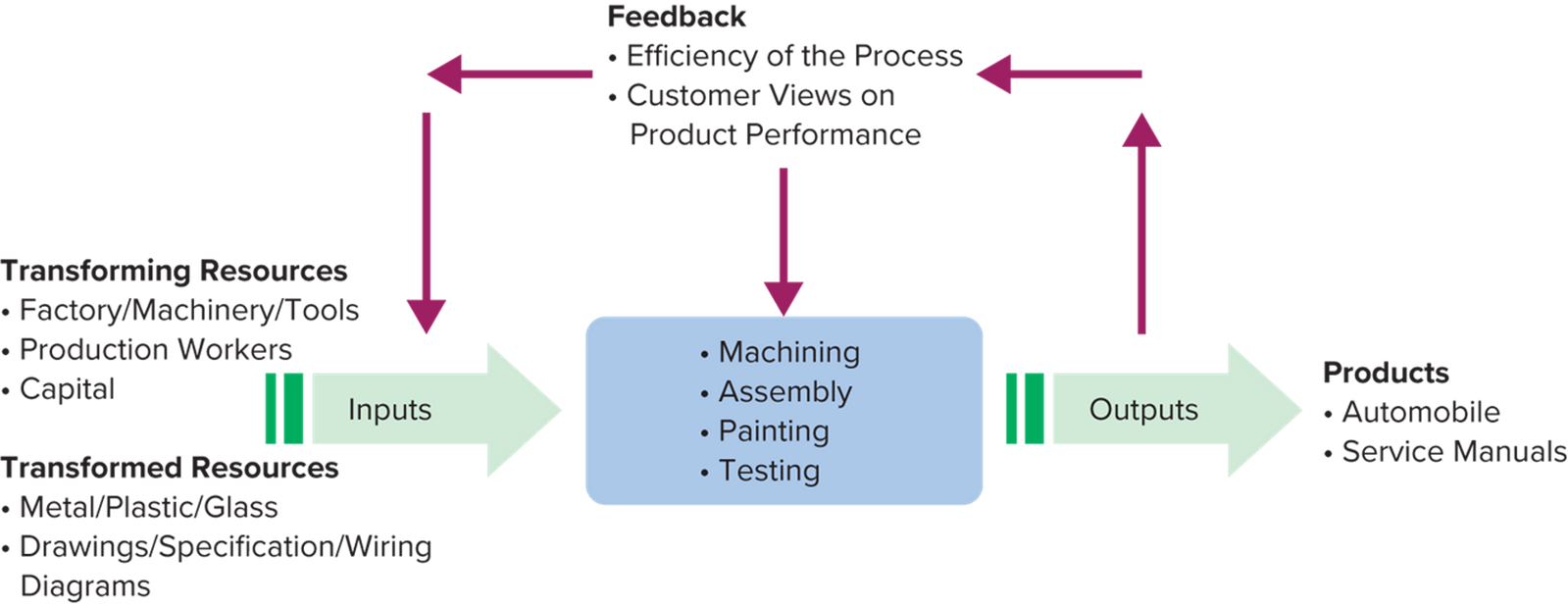
Inputs
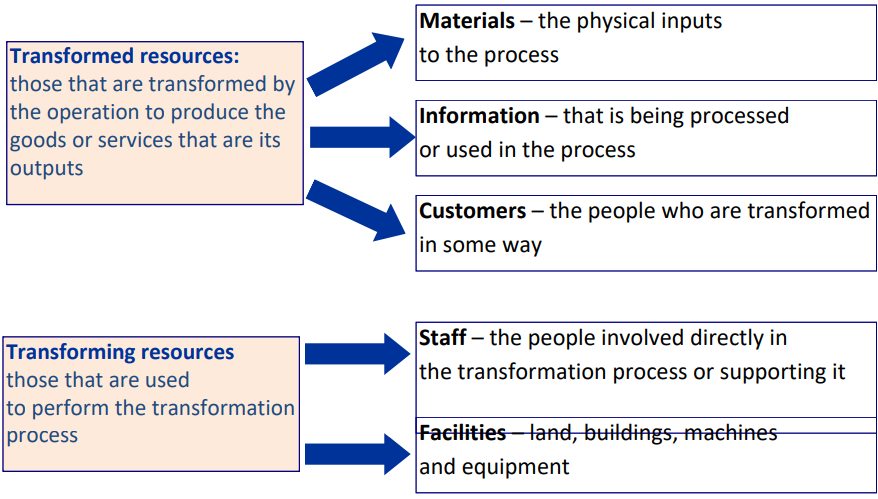
Outputs
Examples of Operations
- Assembly of an iPhone
- Banking
- Flight
- Gym service
- Supermarket shopping
- Healthcare
- Anything that is adding value!
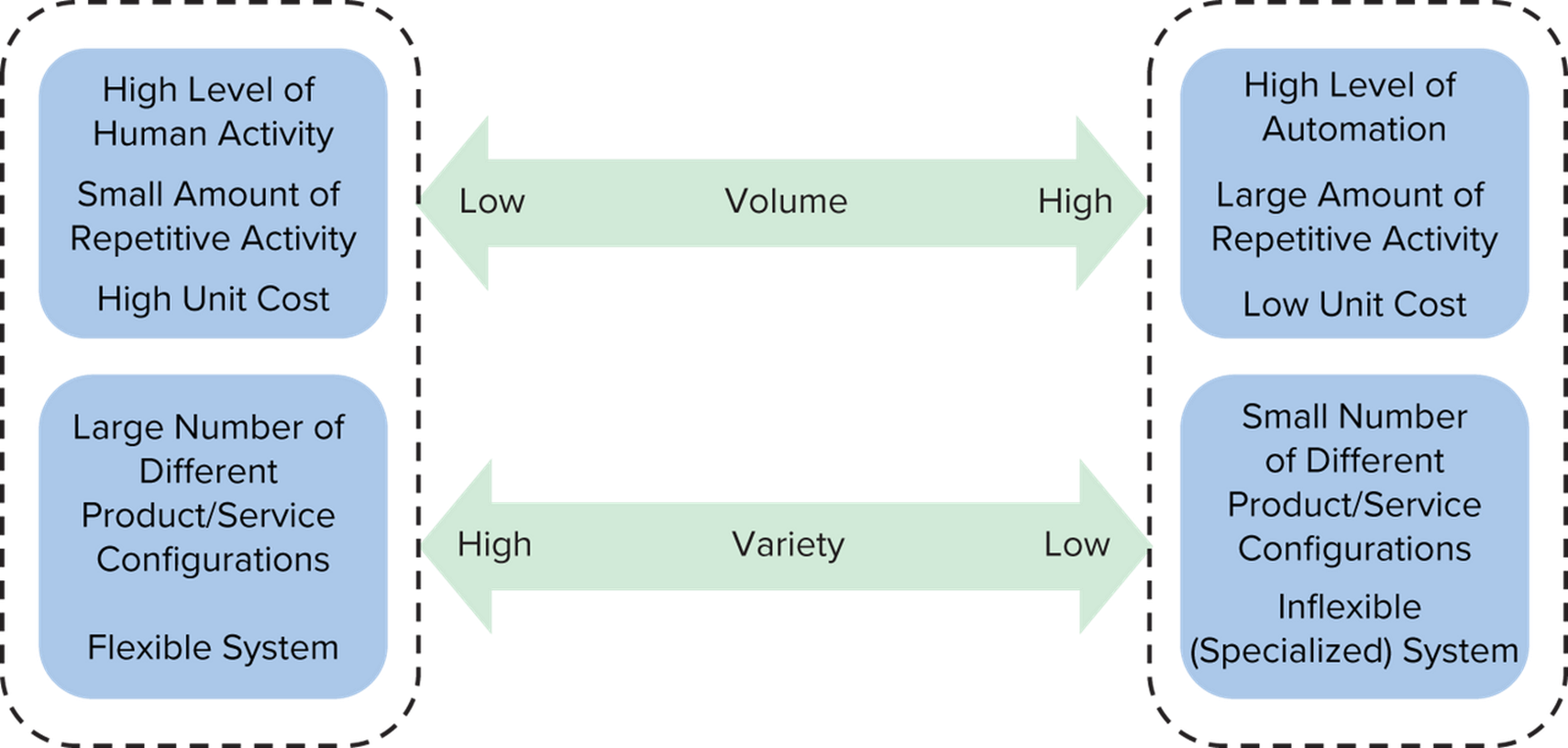
The Volume/Variety of Output
What do Operations Managers do?
Operations Manager Vacancy from Michael Page (example)
- Overall responsibility for the end-to-end processes and delivery across their wide product range
- The production facilities use available data to ensure the right resources and equipment are available to deliver the production schedule.
- Monitoring team productivity weekly to identify and act upon issues arising, using this as a learning to drive improvement.
- Product quality: Setting standards and targets for product quality, ensuring these are met, and delivering continuous improvement.
- Embedding the concept of 'Right-First-Time' into the businesses ' day working practices.
- Productivity & labour efficiency; material utilisation/yield Delivery; on-time in full to customers.
- Adapting to changes to priorities, specifications, quantities and late inputs. Driving continuous improvement initiatives & implementing improvement projects.
- Process improvement - project managing the selection and implementation of better methods and equipment.
- Motivating & developing your team; identifying, arranging & supporting any training needs.
A critical perspective on Operations Management
Operations Management cannot be confined to one organisational function but is distributed across processes in the entire organisation.
Operations Management taking a perspective of:
- Globalization
- Business Integration
- Social Responsibility









